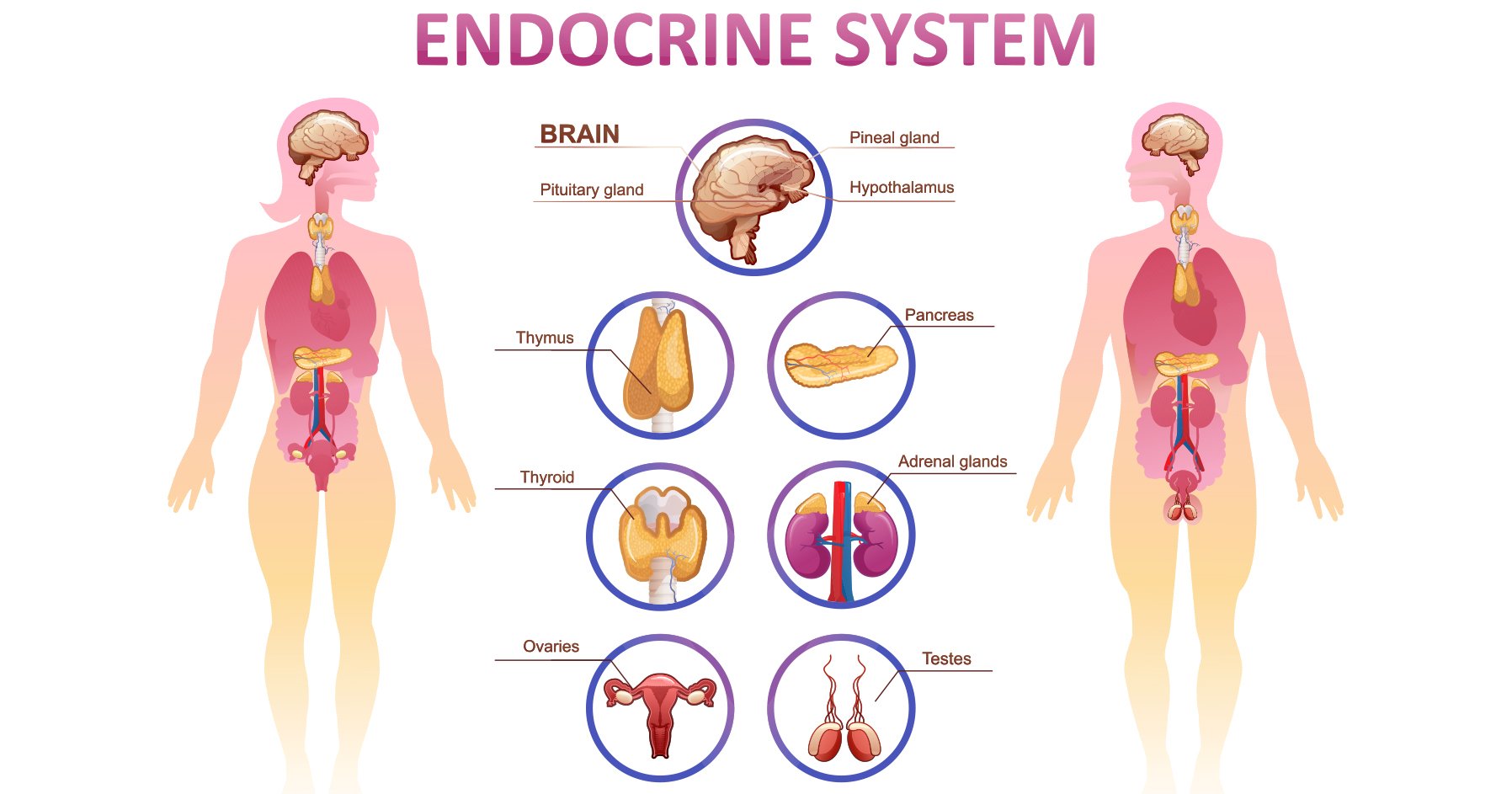
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs. It uses hormones to control and coordinate your body's metabolism, energy level, reproduction, growth and development, and response to injury, stress, and mood. The following are integral parts of the endocrine system Hypothalamus.
Parts of the Endocrine system
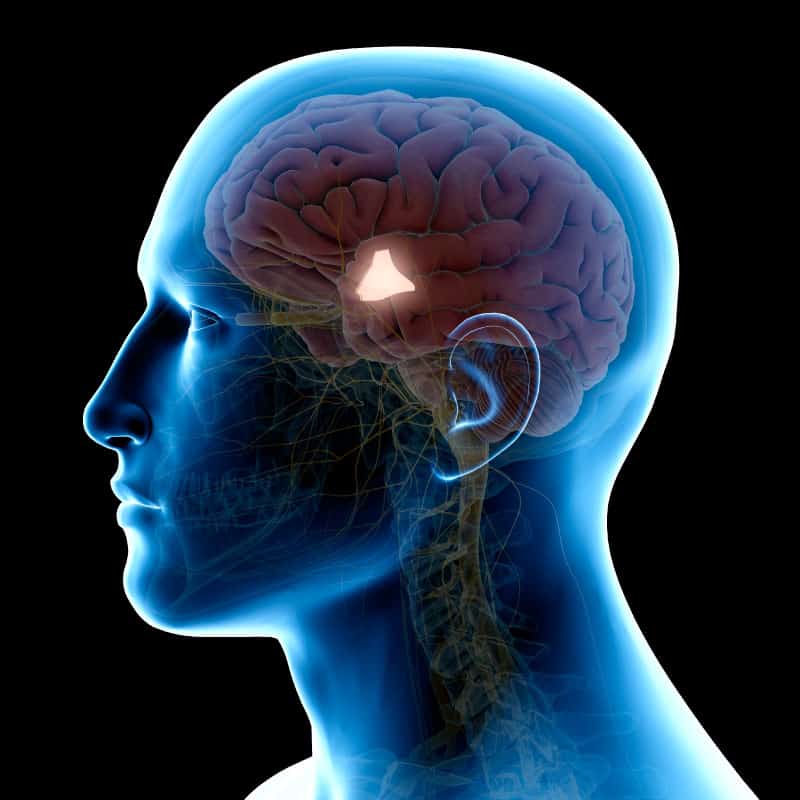
The hypothalamus secretes hormones that stimulate or suppress the release of hormones in the pituitary gland. Your hypothalamus, a structure deep in your brain, acts as your body's smart control coordinating center. Its main function is to keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis. It does its job by directly influencing your autonomic nervous system or by managing hormones.

Your adrenal glands are endocrine glands located on top of your kidneys. They produce many important hormones, including cortisol, aldosterone and adrenaline. The adrenal hormones help regulate several bodily functions including metabolism, blood pressure and your body's response to stress.
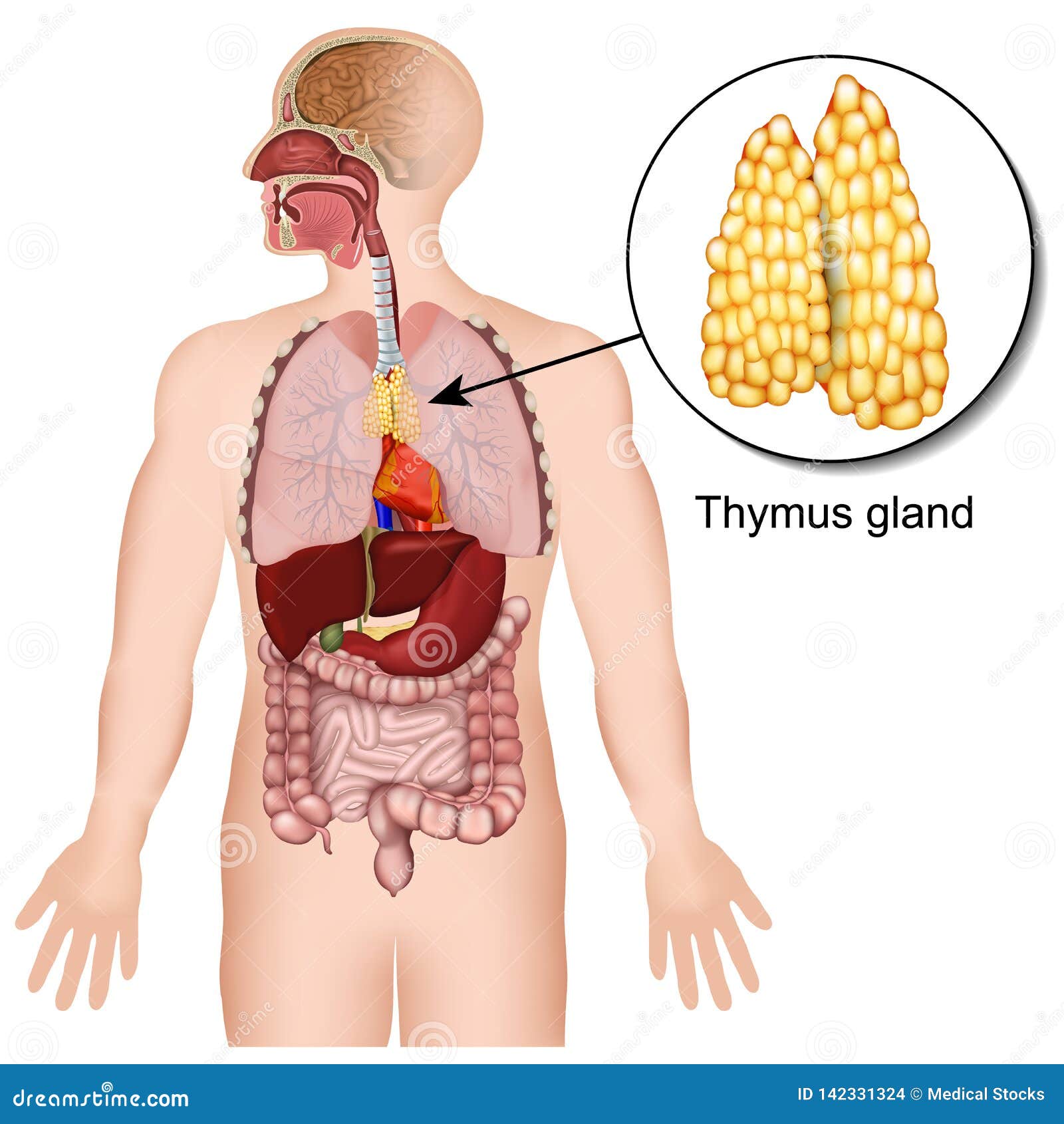
Your thymus gland is also part of your endocrine system. Your endocrine system makes and releases hormones that control the functions of your body. Your thymus produces and releases several hormones including: Thymopoietin: fuels the production of T-cells and tells the pituitary gland to release hormones.
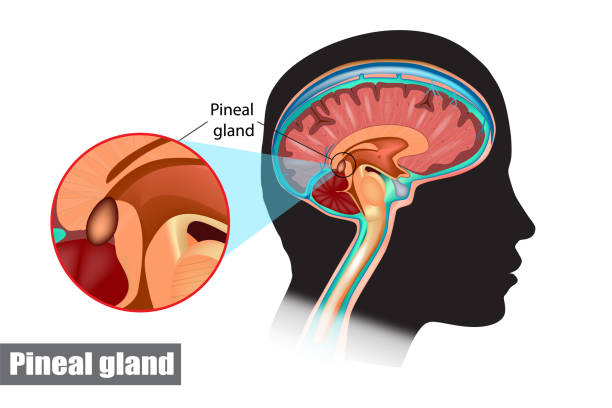
- The main function of the pineal gland is to receive information about the state of the light-dark cycle from the environment and convey this information by the production and secretion of the hormone melatonin.
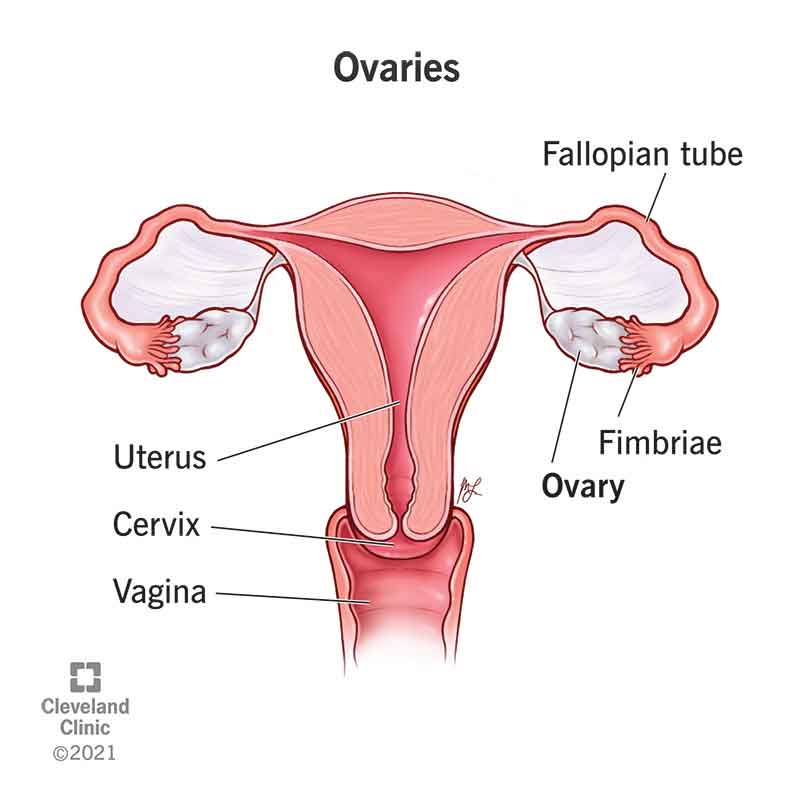
Your ovaries play a critical role in both menstruation and conception. They produce eggs for fertilization and they make the hormones estrogen and progesterone. An ovary releases an egg around the middle of your menstrual cycle (around day 14 of a 28-day cycle) in a process called ovulation.
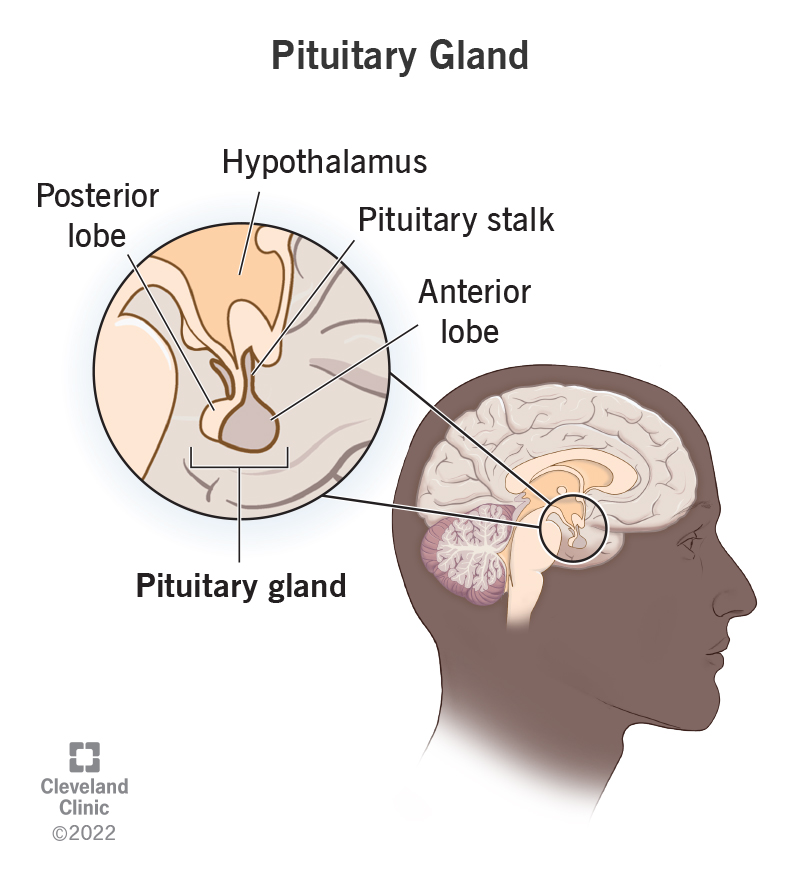
The pituitary gland is sometimes called the "master" gland of the endocrine system because it controls the functions of many of the other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain.
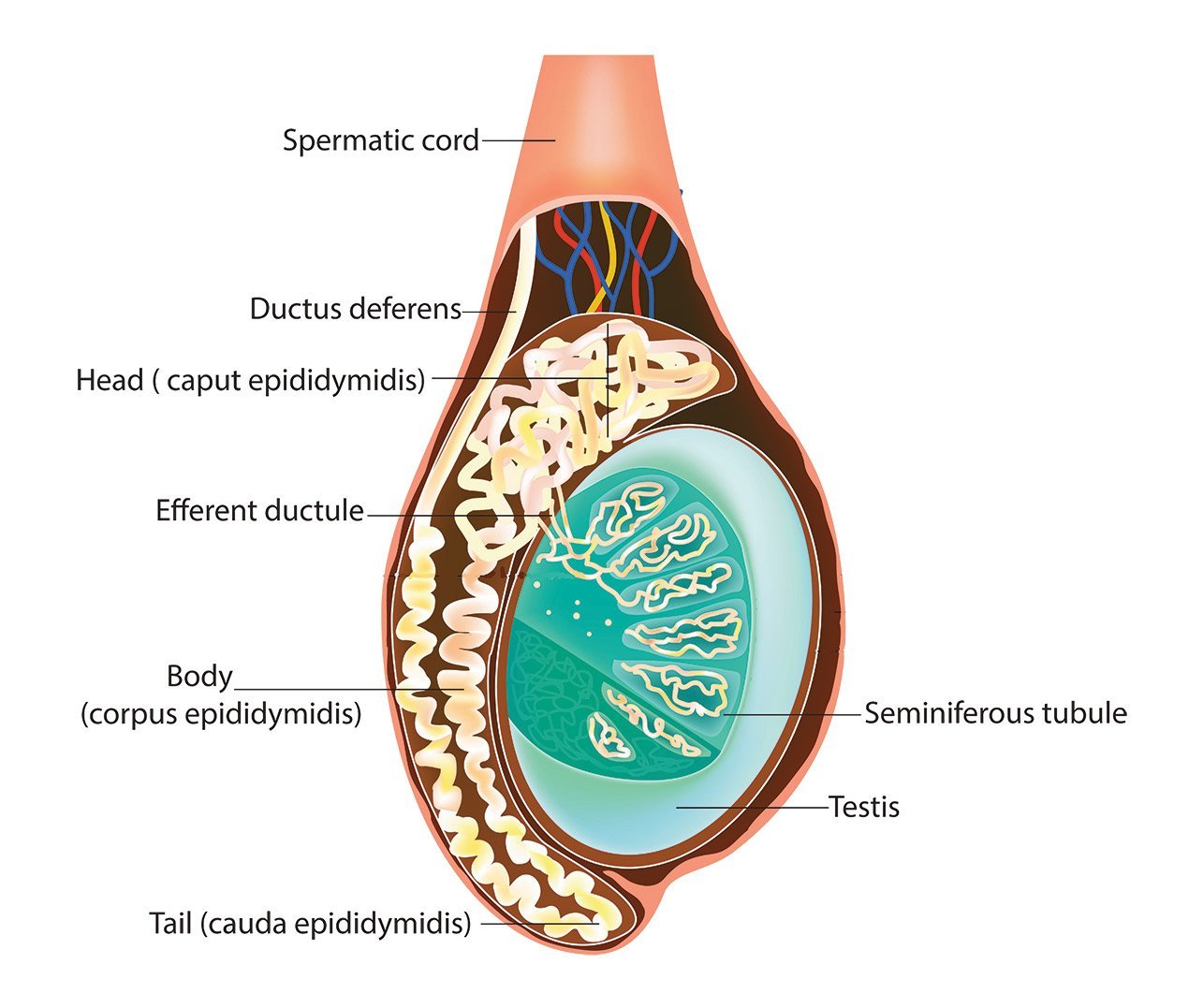
The gonads, the primary reproductive organs, are the testes in the male and the ovaries in the female. These organs are responsible for producing the sperm and ova, but they also secrete hormones and are considered to be endocrine glands.
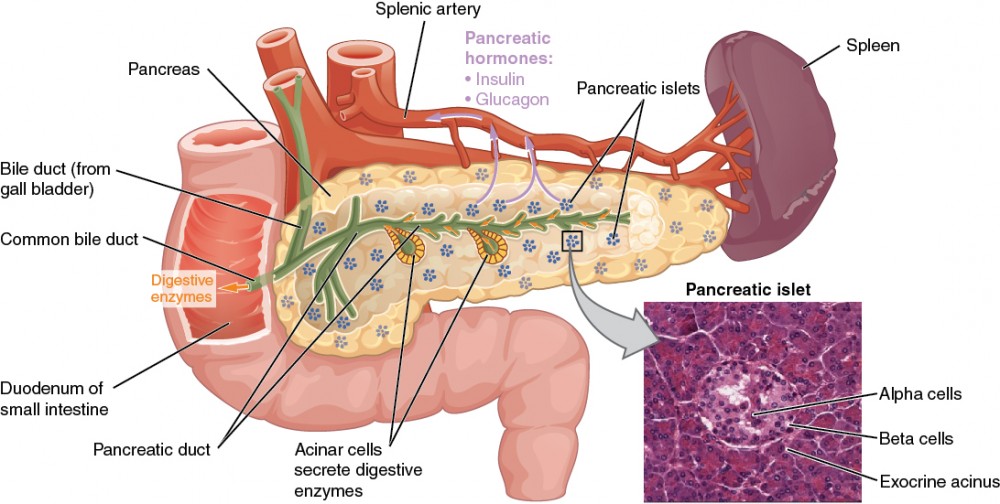
The endocrine component of the pancreas consists of islet cells that create and release important hormones directly into the bloodstream. Two of the main pancreatic hormones are insulin, which acts to lower blood sugar, and glucagon, which acts to raise blood sugar.
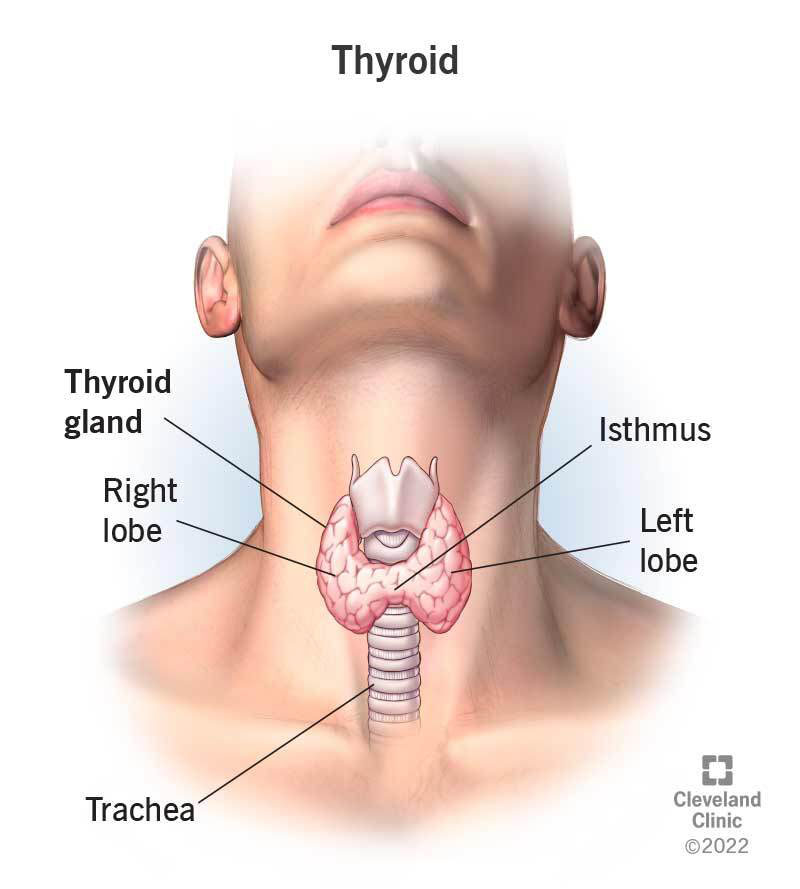
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in the base of your neck. It releases hormones that control metabolism the way your body uses energy. The thyroid's hormones regulate vital body functions, including ,Breathing ,Heart rate, Central and peripheral nervous systems, Body weight, Muscle strength, Menstrual cycles, Body temperature, and Cholesterol levels
Body cavity of the Endocrine system
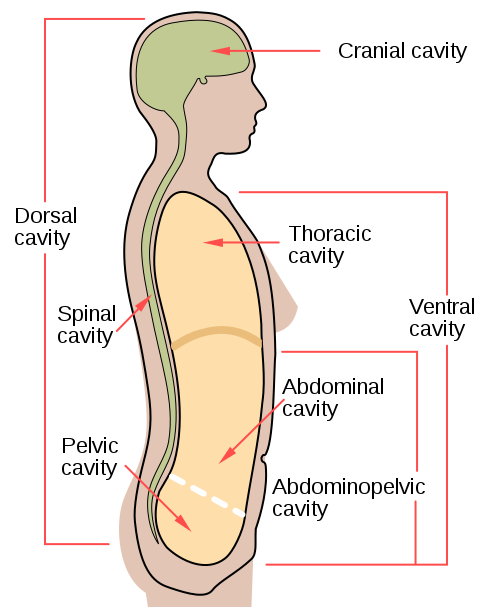
The abdominal cavity is not contained within bone and houses many organs of the digestive and renal systems, as well as some organs of the endocrine system, such as the adrenal glands.
Cavities that are the same part of the Endocrine
Cranial cavity includes : Pituitary gland, Pineal gland, and hypothalamus
Thoracic cavity includes: Thymus and Pancreas
Abdominal cavity includes: Thyroid and Adrenal glands
Pelvic cavity includes: Ovaries and Testes
Endocrine planes and anatomy
an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections


an imaginary line dividing the body into superior and inferior parts or top and bottom.
A vertical plane running from side to side; divides the body or any of its parts into anterior and posterior portions.

Tissues of the endocrine
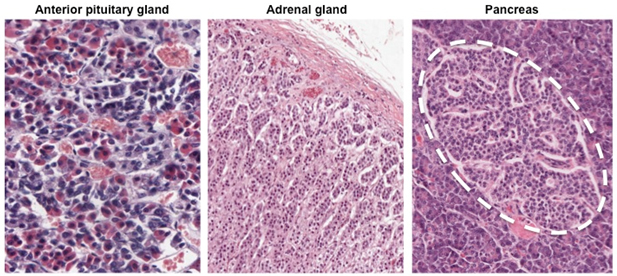
EPITHELIAL TISSUE forms the parenchyma of thyroid, parathyroid, anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis), adrenal cortex, pancreatic islets, and liver. The epithelial nature of these cells is reflected in their organization into cords or clumps, with cells attached laterally to neighboring cells as in surface epithelium.
- The endocrine system is made up of organs called glands.
- Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland of the body.
- There are other glands that contain endocrine tissue and secrete hormones, including the pancreas, ovaries, and testes.