Nyandria
Muscular Systems Anatomical Directions and Body Cavities
What is Muscular System?
The muscular system is composed of specialized cells called muscle fibers. Their predominant function is contractibility. Muscles, attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels, are responsible for movement. Nearly all movement in the body is the result of muscle contraction.
Where is the Muscular System?
The muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body. Attached to the bones of the skeletal system are about 700 named muscles that make up roughly half of a person's body weight. Each of these muscles is a discrete organ constructed of skeletal muscle tissue, blood vessels, tendons, and nerves.
Example: Myalgia means muscle pain.
Myositis means inflammation of muscular tissue.
Muscular dystrophy is an inherited muscular disorder, occurring most often in males, in which the muscle tissue degenerates over time, resulting in complete paralysis.
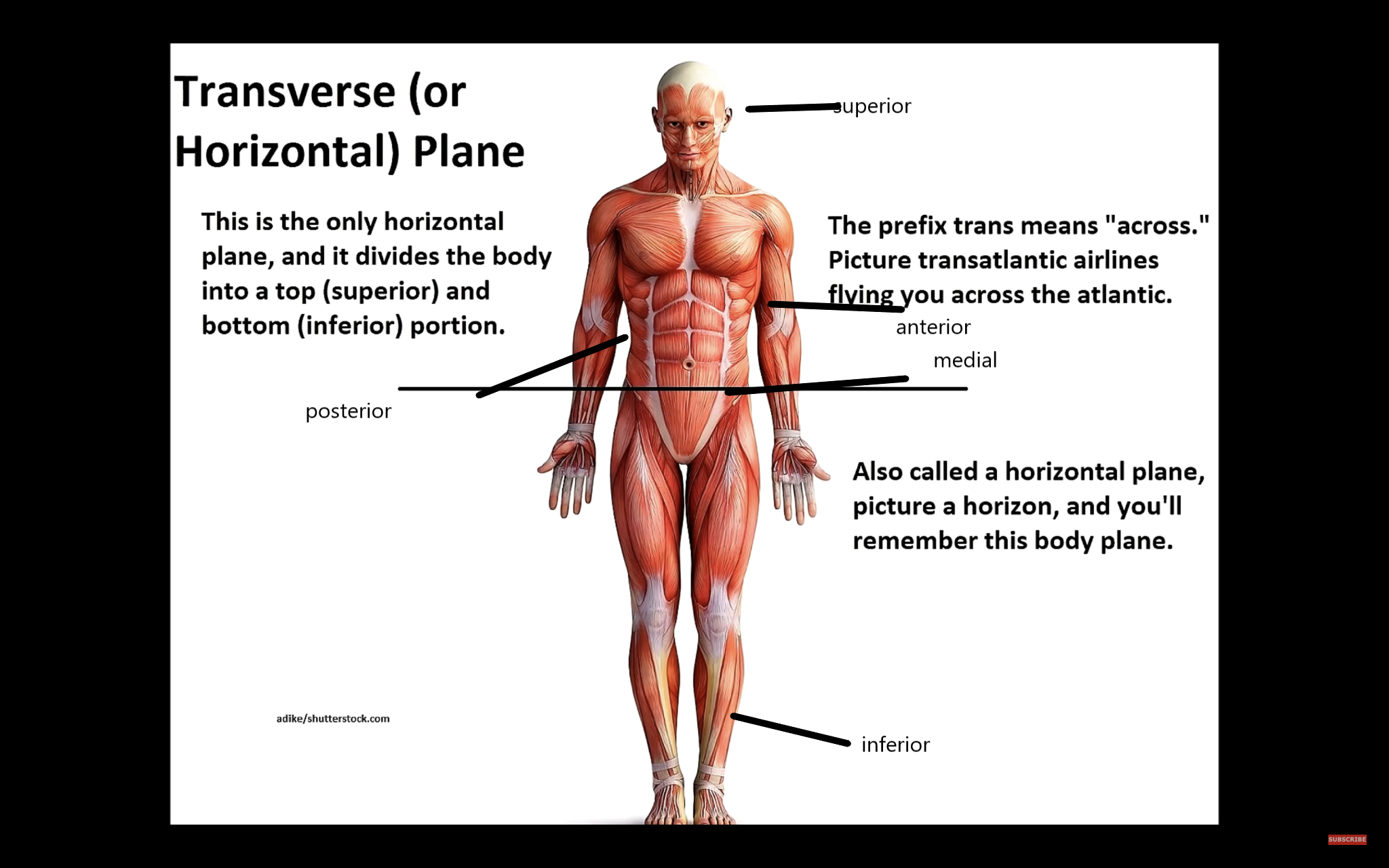
Where is the transverse plane the Muscular System?
Transverse abdominal muscle starts at either side of your spine, wraps around your torso, connects to your ribcage and ends at the middle line of your abdomen.

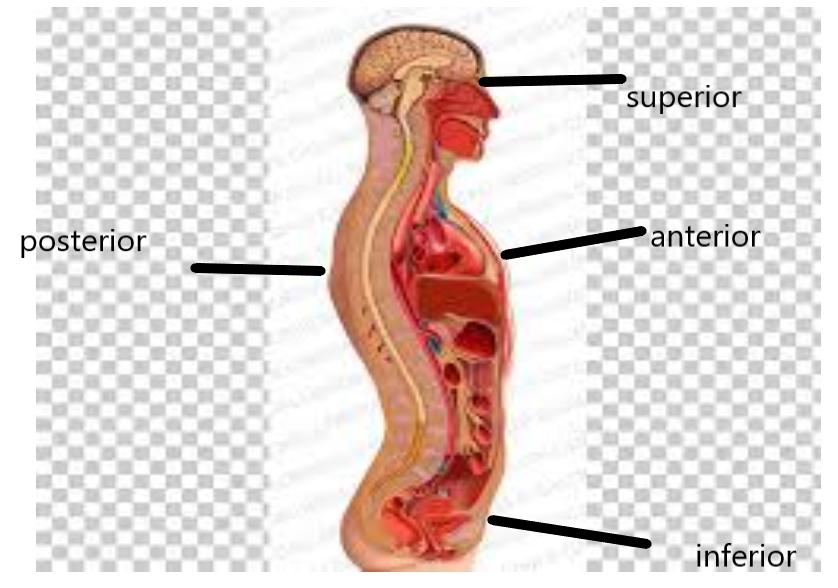
Where is the sagittal plane in the Muscular System?
The Sagittal plane passes through the body front to back. It divides it into left and right. Movements in this plane of motion are up and down movements, for example, flexion and extension. If you move your straight arm forwards and upwards from the hip, this is shoulder flexion.
link- https://www.healthline.com/health/body-planes#what-they-are

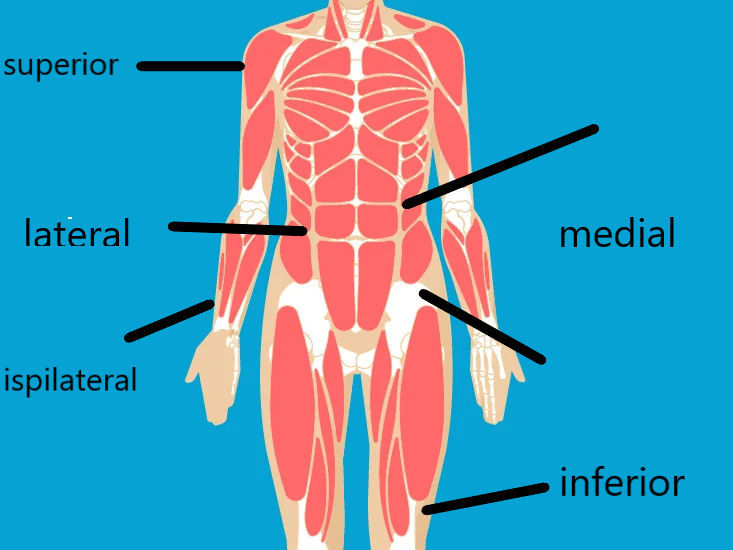
Where is the frontal plane in the Muscular System?
The frontal plane divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) sections. Movements that occur in the frontal plane are lateral or side-to-side movements. These include: Abduction: Moving (or moving a limb) laterally and away from the midline of the body.
Body Cavities
- Skeletal: As part of the musculoskeletal system, these muscles work with your bones, tendons and ligaments. Tendons attach skeletal muscles to bones all over your body.
- Cardiac: These muscles line the heart walls.
- Smooth: These muscles line the insides of organs such as the bladder, stomach and intestines.
What body cavity is the muscular system in?
thoracic cavity, also called chest cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body.
Link - https://www.britannica.com/science/thoracic-cavity
What is the main part of the muscular system?
The muscular system is composed of specialized cells called muscle fibers. Their predominant function is contractibility. Muscles, attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels, are responsible for movement.
- Shoulder and back muscles. Slouching over our screens and sitting too much makes it crucial to work your shoulder and back muscles. ...
- Chest and arm muscles.
- Abdominal muscles.
- Leg muscles.
- Calves muscles.
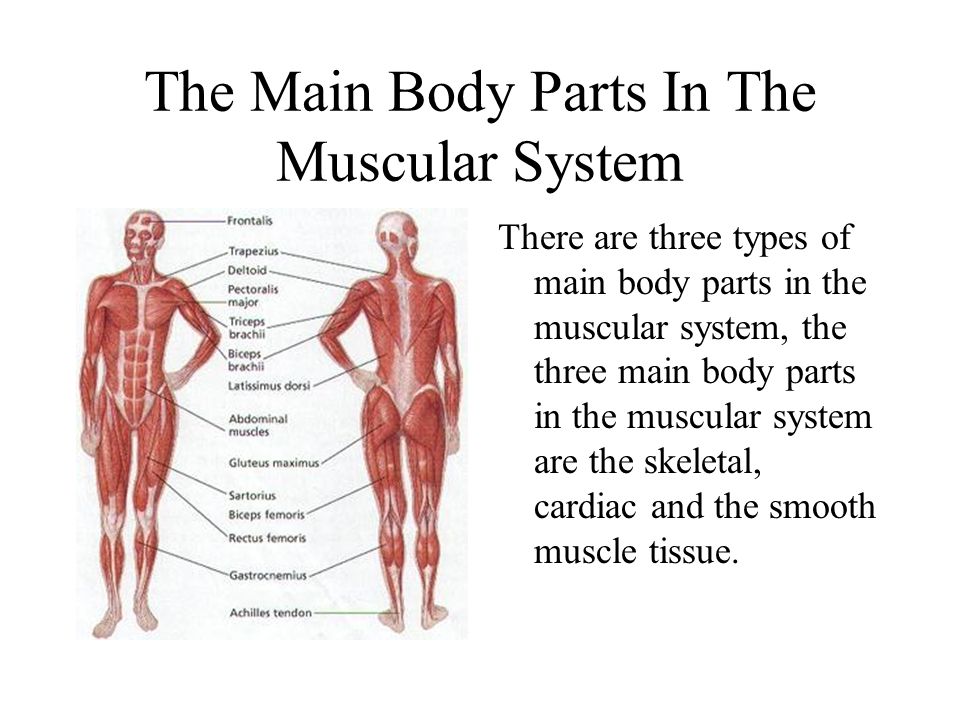
What is the musculoskeletal system?
Your musculoskeletal system includes bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments and soft tissues. They work together to support your body's weight and help you move.
link - https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/12254-musculoskeletal-system-normal-structure--function#:~:text=What%20is%20the%20musculoskeletal%20system,posture%20and%20help%20you%20move.
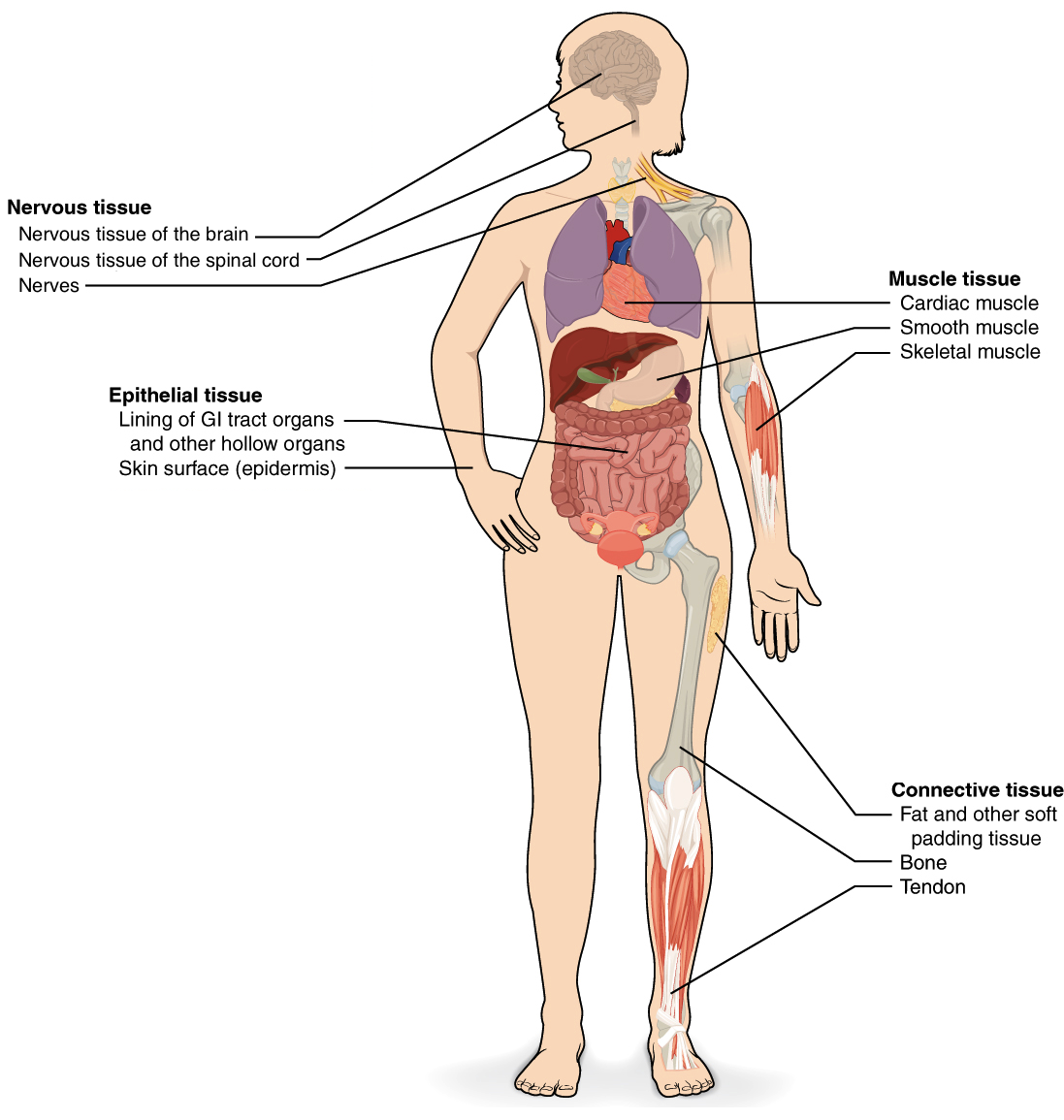
What are muscle tissues?
Muscle tissue is composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts. The tissue is highly cellular and is well supplied with blood vessels.
Link -https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/cells_tissues_membranes/tissues/muscle.html#:~:text=Muscle%20tissue%20is%20composed%20of,well%20supplied%20with%20blood%20vessels.
video
https://youtu.be/21bgO104QVU
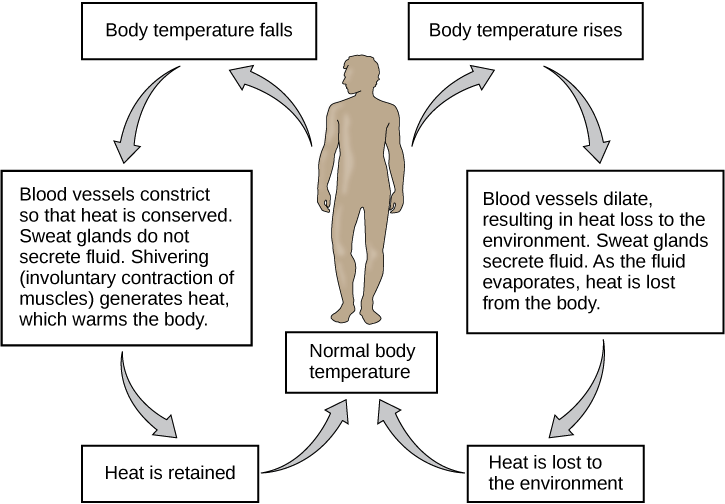
How does muscle organ system responds to changes in body temperature?
Muscles contact and rapidly, which generations heat to keep you work. The hair on your skin rises, trapping more air, which is a good insulator, near your skin. These responses to decreased body temperature explain why you shiver, get “goose bumps,” and have cold, pale extremities when you are cold.
link:
How does muscular organ systems responds to changes in ph?
The model suggests that reducing pH has two opposing effects, a decrease in attachment favoring a decrease in muscle force and a decrease in detachment favoring an increase in muscle force.
link: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30382520/#:~:text=The%20model%20suggests%20that%20reducing,an%20increase%20in%20muscle%20force.
How does muscle systems responds to a change in blood pressure?
Skeletal muscles also play a key role in the movement of blood around the body. Veins embedded within a muscle are compressed during contraction of that muscle, causing an increase in blood pressure due to the presence of one-way valves within the veins. This increase in pressure drives the blood towards the heart. The skeletal muscles of the legs are particularly important skeletal muscle pumps as they prevent pooling of the blood in the feet and calves due to gravity.
Link: https://med.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Anatomy_and_Physiology/Anatomy_and_Physiology_(Boundless)/18%3A_Cardiovascular_System%3A_Blood_Vessels/18.7%3A_Blood_Flow_Through_the_Body/18.7C%3A_Blood_Flow_in_Skeletal_Muscle#:~:text=Skeletal%20muscles%20also%20play%20a,the%20blood%20towards%20the%20heart.
How does the muscle systems respond to a change in blood sugar?
List the normal levels for the vital sign as it pertains to muscular system?
- Body temperature.
- Pulse rate.
- Respiration rate (rate of breathing)
- Blood pressure (Blood pressure is not considered a vital sign, but is often measured along with the vital signs.)
- link:https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure
Explain how the organ system responds to a rise in that particular?
Explains how the muscular system responds to a fall in that particular vital sign.
The four main vital signs routinely monitored by medical professionals and health care providers include the following: Body temperature. Pulse rate.
link:https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure